Artificial Intelligence
To understand Artificial Intelligence (AI), first we will discuss the concept of intelligence. Knowledge and intelligence are two different things; knowledge means to know, whereas intelligence is the application of knowledge to solve problems using algorithms.
The word ‘Artificial’ in the term Artificial Intelligence refers to something created by humans, as opposed to natural intelligence. AI is intelligence exhibited by machines. It mimics cognitive functions like learning and problem-solving, typically associated with human intelligence.
Some notable examples of AI applications include advanced search engine algorithms like Google, Natural Language Processing (NLP) technologies such as Siri and Alexa, and self-driving vehicles that are transforming the automotive industry.
Types Of Artificial Intelligence
- Weak or Narrow Artificial Intelligence: AI designed for specific tasks, like self-driving cars and voice assistants (Siri, Alexa), falls under this category. It’s the most common form of AI in use today, particularly in automation and customer service applications.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): AGI refers to the theoretical concept of AI systems possessing human-like cognitive abilities across multiple domains. It remains a future goal for AI researchers.
Wonders Of Artificial Intelligence
- Automation: AI is capable of automating repetitive tasks, leading to increased business productivity and cost savings. Examples include AI-driven manufacturing processes and customer support systems.
- AI-Powered Accessibility: AI improves accessibility for people with disabilities, such as through real-time translation or tools that assist individuals with visual impairments.
- AI in Transportation: AI optimizes traffic systems and powers autonomous vehicles, enhancing both public safety and transportation efficiency.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP allows machines to understand and generate human language, powering virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, along with AI-driven chatbots used in customer support.
- Healthcare Advancements: AI is revolutionizing healthcare by assisting in diagnostics, personalizing treatment plans, and predicting patient outcomes. It also aids in analyzing medical images and performing surgeries with precision.
- Enhanced Creativity: AI is contributing to the creation of artificial art, music generation, and literature. Tools like DALL-E and GPT-4 generate creative outputs from simple prompts.
- Predictive Analytics: AI helps businesses by analyzing large data sets to predict future trends, optimize decision-making, and streamline supply chain management.
Challenges and Concerns of AI
- Job Automation: The rise of AI automation poses threats to low-skilled jobs, with AI outperforming humans in repetitive tasks, resulting in widespread job displacement.
- Loss of Human Skills: Relying too heavily on AI could lead to a decline in human creativity and decision-making abilities.
- Environmental Impact: The energy demands of large AI models and data centers can negatively impact the environment, contributing to climate change.
- Misinformation: AI tools can be used to create deepfakes and spread misinformation, which can undermine public trust and destabilize democratic systems.
- AI Arms Race: The development of AI-powered autonomous weapons raises ethical and security concerns. The race to develop these technologies may have far-reaching consequences for global security.
Machine learning vs Deep learning
Deep learning and machine learning both falls under the umbrella of Artificial Intelligence, but they represent distinct approaches to train AI systems. The primary distinction lies in their training data, machine learning typically relies on smaller, structured datasets, whereas deep learning leverages larger, unstructured datasets.
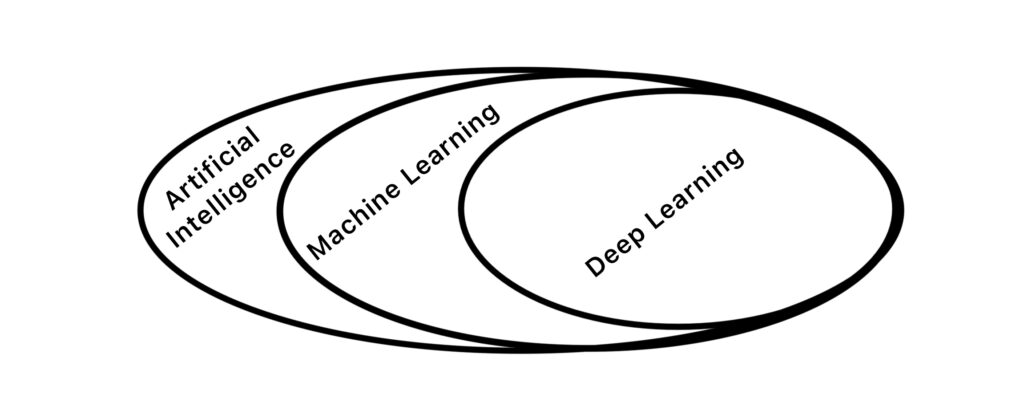
Machine learning enable computers to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data. Wheras Deep learning utilizes deep neural networks, which are algorithms inspired by the structure of the human brain. These networks have many layers, allowing them to automatically learn representations of data.
| Machine Learning | Deep Learning |
| It uses various algorithms like Decision Trees, k-Nearest Neighbors etc. | It primarily uses Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) |
| It requires manual selection and engineering of features. | It automatically learns relevant features from raw unstructured data. |
| ML relies on structured data. | Capable of handling unstructured and high-dimensional data effectively. |
| Many ML models are interpretable. | DL models are less interpretable due to their complex neural network. |
| It generally reuires less computational resources | Requires significant computational resources |
| It is generally trained on smaller datasets. | Large unstructured dataset is required to train such complex models |
| Its area of application includes finance, healthcare, marketing and more. | It is particularly powerful in tasks like image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous systems |
Ethical considerations
AI ethical considerations encompass a set of principles and guidelines that guide the development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence technologies in a responsible and morally sound manner. These considerations aim to address potential societal, legal, and individual impacts of AI systems. Key aspects of AI ethical considerations includes the following:
- Transparency
- Fairness and bias
- Accountability
- Safety
- Privacy
- Human-Centric Design
- Inclusivity
- Regulatory Compliance
By prioritizing these ethical considerations, developers can contribute to the responsible and sustainable growth of AI technologies, fostering trust among users and addressing societal concerns.
Start a Free course on Artificial Intelligence
from Basics to Advance level
Leave a Reply