What is a computer?
A computer is an electronic device capable of performing calculations, storing data, and processing information to produce results in a specified format. It is a versatile machine that has revolutionized industries, communication, and daily life.
A computer primarily consists of three essential components:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The brain of the computer that processes data.
- Monitor: A screen that displays output in a graphical format.
- Keyboard: An input device used to type and interact with the computer.
Computer Organisation
The basic structure of a computer system is represented by a block diagram consisting of five main units: Input Unit, Memory Unit, Control Unit, Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), and Output Unit. These components work together to perform all operations of a computer.
A computer, regardless of its size or type, performs five fundamental functions: input, storage, processing, output, and control.
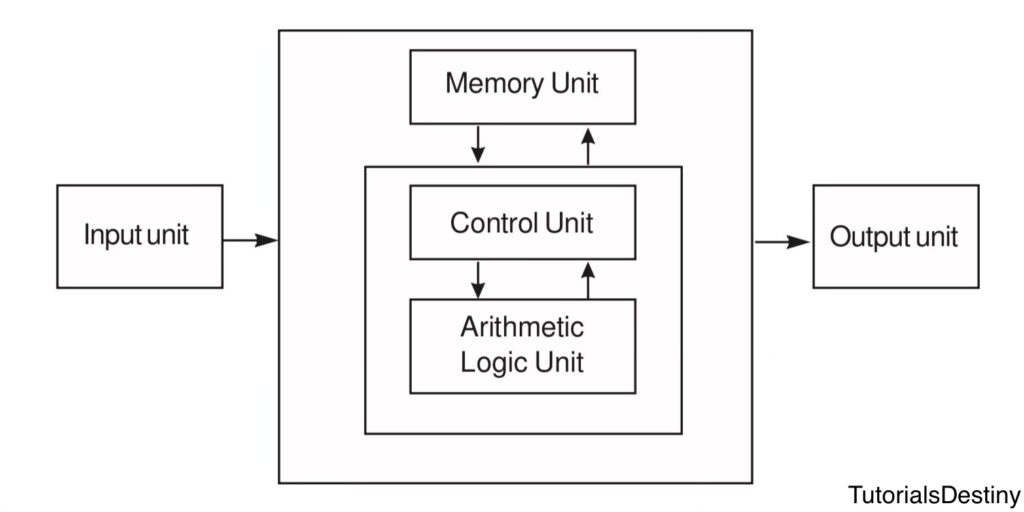
1. Input Unit
The input unit is responsible for receiving data and instructions from the user. It converts the data into a form that the computer can understand and process. Devices such as the keyboard, mouse, scanner, and microphone are commonly used as input devices.
2. Control Unit (CU)
The Control Unit supervises and coordinates all operations of the computer system. It manages the execution of instructions step by step. The CU decides:
- When to accept data
- When to stop receiving data
- Where to store data
- Which operation to perform next
It ensures that all parts of the computer work together in an organized manner.
3. Memory Unit
The Memory Unit stores data, instructions, and intermediate results. It holds information before processing, during processing, and after processing. Memory allows the computer to retain information temporarily or permanently.
4. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
The Arithmetic Logic Unit performs all arithmetic and logical operations in the computer. These operations include:
- Addition
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Division
- Logical operations
- Comparisons
All calculations required for processing data are carried out by the ALU.
5. Output Unit
The output unit presents the processed results to the user. It converts processed data into a human-readable form. Devices such as monitors, printers, and speakers are used to display output.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) and the Control Unit (CU) together form the Central Processing Unit (CPU). The CPU is considered the brain of the computer because it controls all operations and performs all processing tasks within the system.
Evolution of Computers
The evolution of computers spans thousands of years, tracing back to ancient tools and progressing to today’s sophisticated quantum systems.
- Ancient Era:
- Abacus (3000 BC): One of the earliest tools for performing basic arithmetic operations.
- 17th Century:
- The creation of mechanical calculators laid the groundwork for computational devices.
- 19th Century:
- Charles Babbage: Often referred to as the “Father of Computers,” he conceptualized the Analytical Engine, introducing programmability and memory storage.
- Mid-20th Century:
- ENIAC (1945): Among the first electronic digital computers.
- The invention of transistors (1947) and integrated circuits revolutionized computing by making machines smaller, faster, and more reliable.
- Late 20th Century:
- Emergence of personal computers (PCs), mainframes, and minicomputers.
- Operating systems like Windows and Linux made computers accessible to a broader audience.
- 21st Century:
- Mobile computing, cloud technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and quantum computing have reshaped the computing landscape.
Components of computer
Hardwares
Hardwares are physical parts of a computer which we can touch with our hands and are in the physical form.These tangible parts perform various functions within a computer system.
There are basically two categories of hardwares.
- Internal Components:
- Motherboard: The main system board to which other components connect. It includes integrated chipsets, controllers, and sockets for adding new components.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The brain of the computer that processes instructions and controls other hardware.
- Memory (RAM): Temporarily stores data for the CPU to process.
- Storage Devices: Hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs) hold applications and files even after the computer is powered off.
- Controller Cards and Expansion Cards: Plug into motherboard slots to expand capabilities (e.g., video cards, network interfaces).
- PSU (Power Supply Unit): Converts AC from a wall socket into DC to power components.
- External Peripherals:
- Monitors: Display output from the video card, providing a graphical user interface.
- Keyboards and Mice: Accept input from users, allowing text entry and voice command execution.
- Speakers and Headphones: Play sounds generated by the computer.
- Printers and Scanners: Print documents or create digital copies.
- External Storage Devices: Easily connect and disconnect to transfer data between computers.
Softwares
Software is a logical part of a computer which is required to run various tasks. Unlike hardwares, softwares cannot be touched with our hands. It has no physical form.
Computer software can be categorised into two groups:
- System software: It resides between a computer’s hardware and the graphical user interface (GUI). It is responsible for overseeing and governing computer resources, including memory, processor, and network functionality. These softwares can be further divided into the following categories.
- Operating Systems: It serves as a bridge connecting users and computer hardware. Operating systems like WindowsOS, Linux, MacOS, and UNIX illustrate this, with Linux being a notable free and open-source option.
- Device Drivers: Device drivers are software components that enable communication between an operating system and hardware devices. They act as intermediaries, allowing the operating system to interact with and control various hardware components like printers, graphics cards, or storage devices.
- Utility Softwares: It is a category of system software designed to perform specific tasks that enhance the overall functionality and performance of a computer. These softwares typically focus on system management, optimization, and maintenance. Examples include antivirus programs, disk cleanup tools, file management utilities, and system monitoring applications.
- Application software: It is also known as end-user software, refers to programs designed to perform specific tasks for users. These software allow users to interact directly with the computer to accomplish various tasks. Examples include web browsers, MS Office, word processing software, spreadsheets, Adobe Photoshop, and VLC media player.
Types Of Computer (Based on size and performance )
- Supercomputer
- These are super fast computers with extremely powerful processors and memory devices.
- Supercomputers are generally used for Weather forecasting, oil and gas explorations, nuclear fusion, designing launch path for satellites etc.
- Mainframe computer
- These computers are mostly used for commercial purpose by big organisations and financial institutions.
- The name mainframe describes the computer with big frames with high computational power and speed.
- ATM (Automated Teller Machine) is an example of Mainframe computer.
- Minicomputer
- Computers in between Mainframe and Microcomputers in term of power and performance are categories as Minicomputers.
- Minicomputers are compact in size but more powerful than a general purpose Microcomputer.
- Some examples of Minicomputer are: Ipad, Smartphone and touch pads.
- Microcomputer
- All the computers using microprocessors as their CPU are called Microcomputer.
- General purpose laptops and desktops we use are the example of Micocomputers.
Types Of Computer
Based on working principle
- Analog Computers
- The computers where analog (continuous) signal is used to process the calculations are termed as analog computers.
- Examples: photocopier, thermometer, voltmeters, fuel level indicators etc.
- Digital Computers
- Most of the computers which we use in our homes and offices are digital computers.
- These machines works by processing binary digits i.e zeros (0) and ones (1).
- Hybrid Computers
- Hybrid computers are the combination of Digital and Analog computers.
- These computers are mostly used in the industries and organisations.
- Both analog and digital signal are used to process the complex calculations.
- Quantum Computers
- This is an emerging field in computer technology, where computers works on the principle of Quantum mechanics rather than classical mechanics.
- Here information is stored in qubits whereas in Digital computer bits are units of data storage.
Based on Generations
1st Generation (1940–1956) – Vacuum Tube Technology
- Technology Used: Vacuum tubes for circuitry, magnetic drums for memory
- Programming Language: Machine language (binary)
- Key Features:
- Very large and expensive
- Consumed a lot of power
- Produced a lot of heat
- Slow processing speed
- Examples: ENIAC, UNIVAC, IBM 701
2nd Generation (1956–1963) – Transistor Technology
- Technology Used: Transistors replaced vacuum tubes
- Programming Language: Assembly language
- Key Features:
- Smaller, faster, cheaper, and more reliable
- Consumed less power
- Still generated heat
- Examples: IBM 1401, CDC 1604, UNIVAC 1108
3rd Generation (1964–1971) – Integrated Circuit (IC) Technology
- Technology Used: Integrated Circuits (ICs)
- Programming Language: High-level languages (e.g., FORTRAN, COBOL)
- Key Features:
- Much smaller in size
- Increased speed and efficiency
- Lower cost and heat generation
- Examples: IBM 360 series, Honeywell 6000, PDP-8
4th Generation (1971–Present) – Microprocessor Technology
- Technology Used: Microprocessors (VLSI – Very Large Scale Integration)
- Programming Language: High-level languages, Object-oriented programming (C, C++)
- Key Features:
- Personal computers (PCs) introduced
- Graphical user interface (GUI)
- Widespread networking, internet
- Examples: IBM PC, Apple Macintosh, Intel 4004 to current processors
5th Generation (Present and Beyond) – Artificial Intelligence
- Technology Used: AI, Machine Learning, Neural Networks, Quantum Computing (early stages)
- Key Features:
- Natural language processing, robotics
- Advanced decision-making and learning capability
- Still under active development
- Examples: Siri, Alexa, self-driving cars, supercomputers (e.g., IBM Watson)
Conclusion
Computers have become integral to modern life, evolving from basic calculators to advanced systems capable of processing enormous amounts of data in real time. With the rapid pace of innovation, the future holds even greater possibilities for how computing technology can transform the world.