Introduction
Computer memory refers to the storage capacity required for storing and processing data. It is a crucial component of a computer system, responsible for holding digital files such as images, songs, PDFs, and system-related files like BIOS settings, the operating system, and essential software required for the system to function.
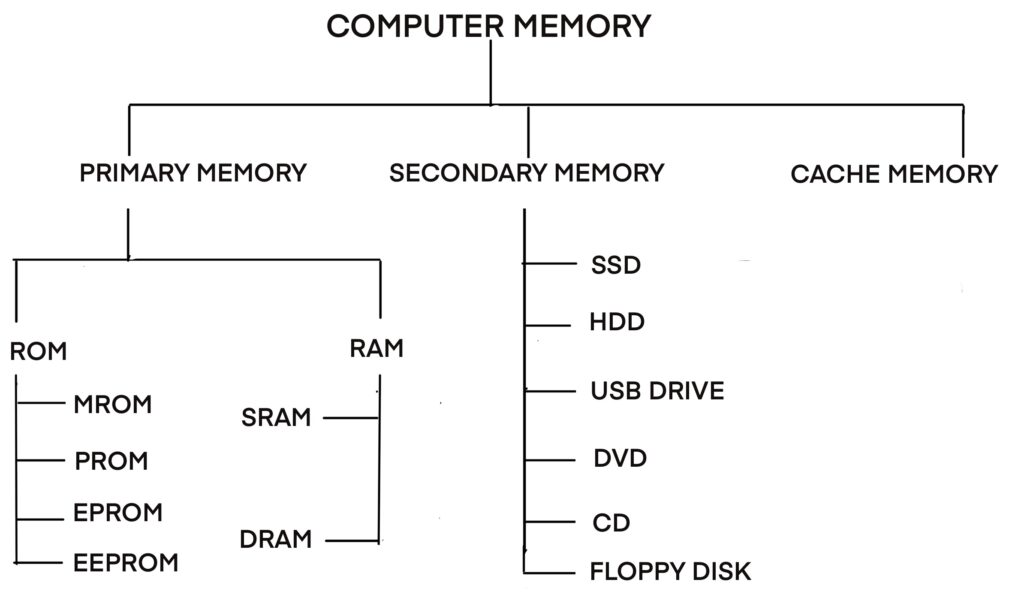
There are mainly two types of computer memory
- Primary Memory
- Secondary Memory
Primary Memory
This type of memory is used to store important files and executables required by the CPU while running system and software applications. Primary memory is also known as main memory, these are semiconductor memories.
Primary memory is mainly divided into two types:-
1. RAM (Random Access Memory)
RAM is a volatile memory, meaning all stored data is lost when the system is powered off. It allows fast read and write operations, making it crucial for system performance.
Types of RAM:
- SRAM (Static RAM) – Faster and more expensive, used in cache memory.
- DRAM (Dynamic RAM) – Slower than SRAM but more affordable, used in main system memory.
ROM ( Read Only Memory )
ROM is a non-volatile memory, meaning it retains data permanently. It is read-only, so the CPU cannot modify its contents. It stores firmware, including the BIOS, which helps in booting up the system.
Types Of ROM
- MROM (Masked ROM)
- PROM (Programmable ROM)
- EPROM (Eraseable Programmable ROM)
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM)
RAM vs ROM
| RAM | ROM |
|---|---|
| It is volatile in nature, data stored is temporary and is lost after powered off. | It is non-volatile in nature, retains data permanently. |
| It is more expensive to buy. | It is less expansive than RAM. |
| Data transfer speed is incredibly fast. | Data transfer is much slower. |
| Size and capacity is compairitively large. | ROM have low capacity and are smaller in size. |
| CPU can read and write on RAM storage. | ROM is a read only memory it cannot be written by CPU. |
Secondary Memory
Secondary memory, also known as external storage, is used for storing data permanently. Unlike primary memory, it does not directly interact with the CPU and is slower but more affordable. These storage devices are non-volatile, meaning they retain data even after the system is powered off.
Types of Secondary Memory Devices:
- HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
- SSD (Solid State Drive)
- USB Drive (Pen Drive/Flash Drive)
- DVD (Digital Versatile Disc)
- CD (Compact Disc)
- Floppy Disk (obsolete)
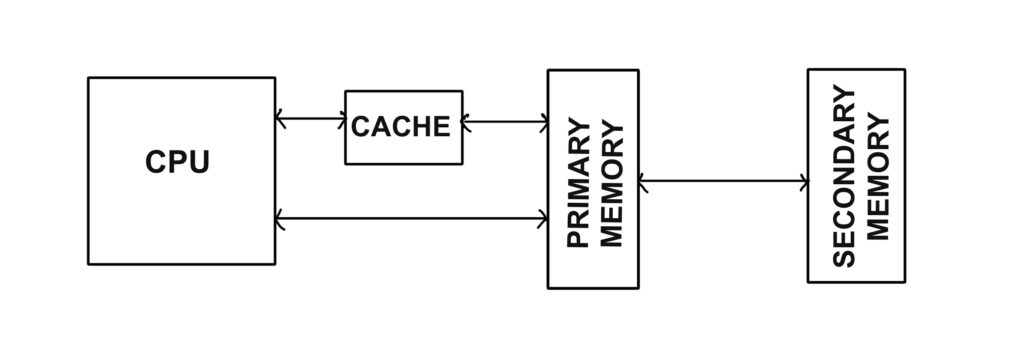
Cache Memory
Cache memory, also known as CPU memory, sits between the main memory and the CPU. It is used to store frequently accessed data for faster processing. Since it is volatile, data is lost when the system is turned off.
When the CPU requires data, it first checks the cache memory. If the data is found, it is retrieved quickly (cache hit). If not, the CPU searches in the primary memory (cache miss), which is slower.
Cache memory is usually embedded on the motherboard or the processor itself to ensure high-speed data access. SRAM (Static RAM) is commonly used as cache memory due to its fast speed.
Levels of Cache Memory:
- Level 1 (L1) – Fastest but smallest in size.
- Level 2 (L2) – Slower than L1 but larger.
- Level 3 (L3) – Slowest among the three but has the largest capacity.
Memory Units
Digital computers store and process data in binary format (0s and 1s). Each binary digit (bit) represents a fundamental unit of memory. The presence (1) or absence (0) of an electrical signal determines the stored value.
| Quantity | Unit |
|---|---|
| 0 or 1 | 1 Bit |
| 4 bits | 1 Nibble or ½ Byte |
| 8 Bits | 1 Byte |
| 1024 Bytes | 1 KB (Kilobyte) |
| 1024 KB | 1 MB (Megabyte) |
| 1024 MB | 1 GB (Giga Byte) |
| 1024 GB | 1 TB (Terabyte) |
| 1024 TB | 1 PB (Petabyte) |
| 1024 PB | 1 EB (Exabyte) |
| 1024 EB | 1 ZB (Zettabyte) |
| 1024 ZB | 1 YB (Yottabyte) |
Conclusion
Computer memory is an essential component that influences a system’s performance and efficiency. The combination of primary memory (RAM & ROM), secondary memory (storage devices), and cache memory ensures smooth operation by balancing speed, cost, and storage capacity.