Introduction
Motherboard as the name suggest is the mother to all other components and daughterboards (wifi cards, graphic cards etc) installed on it. It is the backbone of any computer system and provide base for all other components.
It is also known as base board, logic board, and main board and is the largest PCB (printed circuit board) present in any computer system.
Motherboard accomodates and provides necessary electrical connections to all the major components of a computer system. Chipset available on the motherboard allows CPU, RAM, PCIe devices and other peripherals to talk to each other.
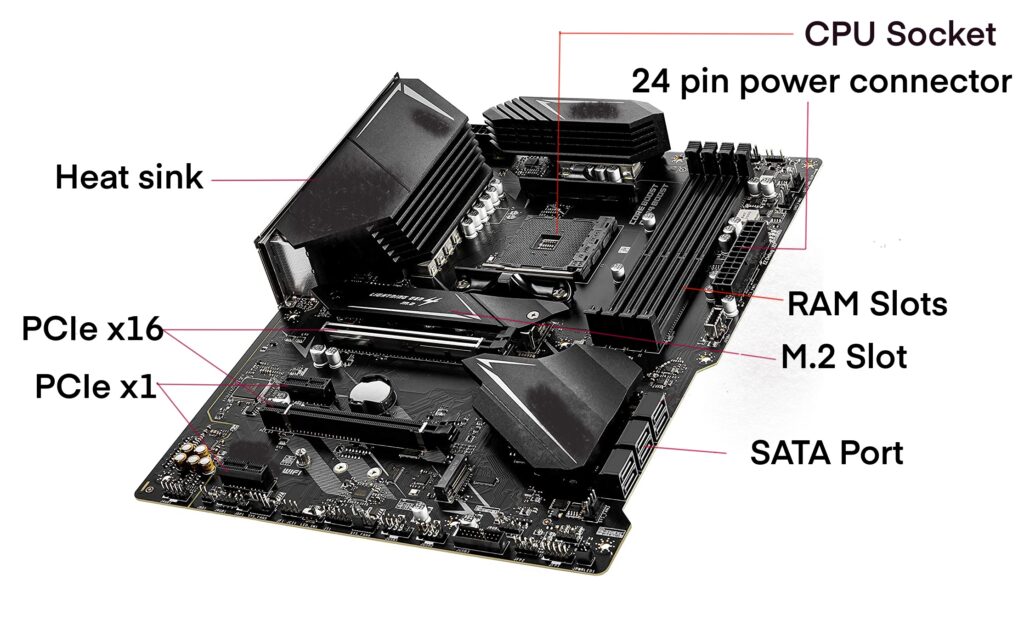
Main sections of a motherboard
CPU Socket
These sockets provides connection between the motherboard and the processor without the need of soldering which make it easy to swap processors.
While installing a new processor you must consider type of CPU socket and the processor for compatibility.
Two common types of CPU sockets are Pin Grid Array (PGA) and Land Grid Array (LGA). PGA type sockets have holes on socket whereas LGA sockets have pins on it and holes on processor.
More the number of pins/holes on the processor more is the electrical connections between the processor and the socket, and thus higher the performance.
Memory/DIMM/RAM slots
DIMM (Dual in-line memory module) slots sometimes also referred as RAM slots are the place where the memory stick goes into the motherboard.
Mostly mordern computers have atleast 4 DIMM slots with two channels. Memory slots often comes in pairs. RAM slots are placed closest to the CPU slots to enable hidh speed data transfer. Slots 1,2 and 3,4 are on two different channels that is why it is always advised to place memory sticks in alternate slots to put them on two different channels to maximise the speed and efficiency.
Memory sticks for desktops and laptops are of DIMM and soDIMM form factors respectively their slots are also different.
PCIE Slot
PCIe (peripheral component interconnect express) is the most standardised way to extend or upgrade your system capabilties. These slots are used to connect add on cards like graphic cards, storage devices, wifi cards etc with the motherboard directly. Different configuration of PCIe slots are available depending on motherboard manufacturers.
Different PCIe configurations are x1, x4, x8, x16, x32.
PCIe can further be classified based on the generations they evolved.
- PCIe 1.0 (2003)
- PCIe 2.0 (2007)
- PCIe 3.0 (2007)
- PCIe 4.0 (2017)
- PCIe 5.0 (2019)
Chipset
This is a set of chips which lies on your motherboard and decide what other components will be supported by your system, number of USB ports support and number/generation of PCIe slots supported.
Chipset provides the pathway for the information to flow on the motherboard. chipsets are always confused with the motherboard but these two are different.There are basically two chipsets faster northbridge and slower southbridge. At present Intel and AMD are the only chipset architecture used by motherboard manufacturers like MSI, Asus and Gigabyte.
Northbridge/Southbridge
These are the chips of chipset present on the motherboard. Norhbridge is faster in data transfer speed. It connects memory and PCIe to the CPU directly via FSB (Front side bus).while southbridge which is slower than northbridge is not directly connected to the CPU. Southbridge connects PCIe, USB and other peripherals to the CPU via nirthbridge.
M.2 slots
These are internally mounted expansion slots used to connect peripherals like wifi cards, SSDs etc.
M.2 formerly known as Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF), is a replacement for Serial ATA connections.
Mostly M.2 slots are used to connect more compact high speed SSDs with M.2 form factor to the motherboard. These M.2 SSD are compact than the SSD/HDD of 2.5” form factor used with SATA 3 connectors.
Types of Motherboards
Motherboard is classified based on the form factor. Form factor of a motherboard refers to its shape and size. Here are some of the prominent types of motherboard based on form-factor.
- Extended ATX
- Standard ATX
- Micro ATX
- Mini ITX
- Nano ITX